Season’s Greetings
And
The Very Best of Wishes,
For The Extreme Delight and Joy
With which you Shelve,
All your Thirsts,
In Twenty-Twelve!
Today THIRST has two meanings (Source - American Heritage Dictionary):
1. A sensation of dryness in the mouth related to a need or a desire to drink
2. An insistent desire or craving or yearning
TRADITIONAL Definitions of Thirst
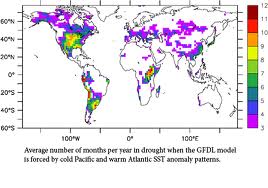
 |
| Source - liberatemedia.com |
Traditional Jewish Water Law (as far back as 3000 B.C.)
- Water is common property "belonging to every man."
- As reflected in the later writings of the Talmud, “Rivers and Streams forming springs, these belong to every man.”
- The “Right of Thirst” is reflected in the Old Testament text in Isaiah: “Let all
you who thirst, come to the water!” Such a policy might be termed a “Rawlsian straw,” in that any traveler in an arid region could foresee a situation where he or she might need water from strangers for survival. In satisfying the Right of Thirst, rules of access still applied, for villagers’ necessary drinking requirements took priority over outsiders’. But outsiders’ thirst took precedence over local grazing and other uses.
Traditional Islamic Water Law
- The Arabic word "Sharia" means "the way of water"
- As the Koran relates: Anyone who gives water to a living creature will be rewarded…To the man who refuses his surplus water, Allah will say: ‘Today I refuse thee my favor, just as thou refused the surplus of something that thou hadst not made thyself.’
African Indigenous Water Law
- While wells and boreholes are often built today for private purposes, they are made available for communal drinking.
- A general fear that denying water to someone could lead the drinking well to be poisoned
Bihar Indian Water Law
- Because of the complex social hierarchy, priority of access and management is much more carefully proscribed than in other cultures along social caste lines. But at times of water scarcity, even access to an upper caste well is allowed.
- The "rule of sharing", however, is widely observed and those in need must be given access to water.
- A divine gift for all of mankind, sharing water is viewed as a spiritual act of generosity – one of the seven kinds of wealth (the ‘saptasantanas’).
Australian Aboriginal Water Law
- Most water sources are sacred parts of the dreamscape.
- Sharing is encoded and embedded within all social relations: trade, marriage, ceremony and others. The code is reciprocity. Not only is the precept ‘always ask’ essential; so too is the fact that people are almost never refused.”
Roman Law
- Rome’s first aqueduct, the Appia, was built in 312 B.C. A priority system ensured that public needs were served first, then private uses, than baths.
- The water was always free for the taking
Source - Salzman, James, "Thirst: A Short History of Drinking Water" (2006). Duke Law School Faculty Scholarship Series. Paper 31. http://lsr.nellco.org/duke_fs/31