Water Storage Reservoirs
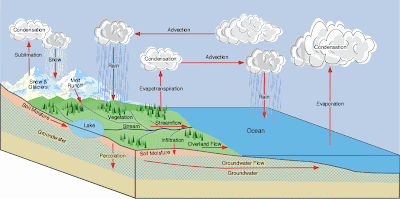 |
| Water Storage Reservoirs Source - www.physicalgeography.net |
Water in the Atmosphere has the smallest residence time
| Reservoir | Average residence time |
|---|---|
| Antarctica | 20,000 years |
| Oceans | 3,200 years |
| Glaciers | 20 to 100 years |
| Seasonal snow cover | 2 to 6 months |
| Soil moisture | 1 to 2 months |
| Groundwater: shallow | 100 to 200 years |
| Groundwater: deep | 10,000 years |
| Lakes | 50 to 100 years |
| Rivers | 2 to 6 months |
| Atmosphere | 9 days |
As shown in the chart, water (in freshwater form) stays the shortest period (just 9 days, on average) in the atmosphere.
Water in the deep ground, on the other hand has the longest residence time of 10,000 years.
The hydraulic Cycle is a Continuous Cycle
The hydraulic cycle never stops. Any efforts to extract water from the atmosphere will only speed-up the hydraulic cycle and reduce water's residence time, in the atmosphere to less than 9 days, on average.
The impact of human efforts to extract water from the atmosphere on Residence times is unknown as no significant extraction is currently possible or done. The efforts at seeding rain have so far been very localized efforts
No comments:
Post a Comment