The Deuterium/Hydrogen Ratio
 |
| Source - nasa.gov |
Much of the Earth's hydrogen exists in two isotopes, namely, the commonly available Hydrogen and as "heavy" hydrogen (Deuterium). 0.015% of ocean water is heavy water i.e. made up of deuterium and oxygen.
Our bodies also contain about 5 grams of deuterium which is thought to be harmless to us in that quantity. At higher levels heavy-water inhibits cell function and is, thus, harmful to the human body.
Meteors and Comets
 |
| Comet Lulin Source - Guardian.com.uk |
Both meteors and comets contain water. Vaporization of the water, as a comet comes close to the sun gives comets their distinctive 'tail.
Meteors, on the other hand, contain only small quantities of water that land on Earth, if the meteor is not vaporised in the atmosphere.
Meteors are named for their originating star and the pieces that land on Earth are called meteorites.
Meteorite showers occur almost annually.
Differences in Water carried by Comets and Meteors
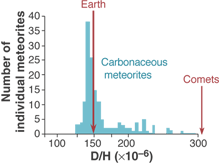 |
| Source - Science Magazine 10 Aug 2001 The Origin of Water by Francois Robert |
Analysis of the water contained on meteorites and comets clearly shows that meteorites contain water in the same deuterium/hydrogen ratio as exists on Earth.
The water on Earth, thus, originated in meteorites.



